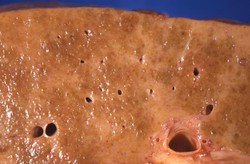
Cirrhosis is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the United States. In that country, it afflicts more than five million individuals and is the seventh leading cause of death in adults between the ages of 25 and 64. The condition develops from long-term scarring and injury of that organ [1].
There are many possible reasons for the infirmity. In the United States, it is most commonly the result of excessive alcohol intake or viral hepatitis. It may also occur from fatty liver disease, autoimmune conditions, bile duct disorders, and injury to the organ from drugs. Moreover, hereditary abnormalities can lead to it [1].
Despite this distribution of the disease, a fifth of patients with it have cryptogenic cirrhosis in which its etiology is uncertain [1].
The liver is the largest organ in the human body [1].



 The Reality of Aspirinon 05/24/2021
The Reality of Aspirinon 05/24/2021
 An Old Microbeon 03/31/2021
An Old Microbeon 03/31/2021
 Coronavirus and Mental Illnesson 02/14/2021
Coronavirus and Mental Illnesson 02/14/2021
 Acute Ischemic Strokeon 12/25/2020
Acute Ischemic Strokeon 12/25/2020


Comments