Pain on the back of the head can be caused by benign issues, such as increased muscle tension, or by serious health conditions, such as a bleeding within the brain. Examples of causes of a sudden pain on the back of the head are migraine attack, severe dehydration, whiplash and rupture of a brain aneurysm. Chronic pain on the back of the head can be caused by emotional or physical stress, bad posture, herniated disc in the neck spine and brain tumor. When trying to narrow down the causes, think when your headache appeared for the first time, what are its triggers and relievers and where does the pain spread.

Headache on the Back of the Head
by greentree
You may be able to figure out the cause of headache on the back of the head from a combination of symptoms.
What Causes Headache on the Back of the Head?
Causes of a sudden headache:
- Migraine
- Severe dehydration
- Whiplash
- Ruptured brain artery aneurysm, stroke
Causes of a chronic headache:
- Stress
- Bad posture
- Herniated disc in the neck spine
- Brain tumor
Below, the causes of pain on the back of the head are listed as:
- Newly appearing
- Episodic
- Chronic recurrent
- Constant
Newly Appearing Pain on the Back of the Head
If you have a newly appearing severe headache, call an ambulance (911 in US) right away and do not seek for online help.
Sinusitis can sometimes cause pain on the back of the head. Pain on the top of the head, front or face, and stuffy nose are other likely symptoms.
Cervicogenic headache. A herniated disc, injury, tuberculosis or cancer in the neck spine can also cause pain on the back of the head. Surgical repair of the spine is usually successful.
Enlarged lymph nodes behind the ears in bacterial tonsillitis or infectious mononucleosis can be painful. Sore throat is the main symptom in both infections. Fungal infection of the scalp (Tinea capitis),folliculitis, and shingles (Herpes zoster) can cause pain and itchy rash on the back of the head.
Brain tumor or cyst in the back part of the brain can cause slowly progressing headache that is worse in the morning. Neurological problems, like muscle weakness, problems with balance and mental changes, are often present before headache.
Within few hours after a head injury, an epidural hematoma can cause one-sided pain on the back of the head. Other common symptoms are dizziness, nausea, vomiting, seizures, impaired vision on one side, weakness or numbness in a limb. An urgent surgery is usually required.
Infectious meningitis or encephalitis often starts with pain and stiffness at the back of the neck, high fever, nausea and sensitivity to light (photophobia). When bacterial meningitis is suspected, antibiotics should be taken right after a sample of blood is taken and before lumbar puncture and imaging investigations, since early onset of treatment usually has a good success, and late treatment might not prevent complications or death. Within hours, headache can spread over the entire head.
Infection of the middle ear and rubella can cause pain on the back of the head.
Stroke or ruptured brain aneurysm may cause sudden (within a minute) severe, constant pain on the back of the head. An urgent surgery is usually required. Rarely, a sudden, severe headache that develops to full intensity within few minutes can appear without a know reason; this is called primary thunderclap headache.
Whiplash is a neck injury after a fall or car accident resulting in pain in the neck and back of the head. An orthopedist can tell which investigations may be needed. A physiotherapist can contribute to recovery, which may last from several weeks to months.
Episodic Headache
Bad posture, eye strain or other physical or psychological stress can trigger tension headache, pressure-like pain, which can be limited to the back of the head (more or less symmetrically).
Migraine headache can be limited to the back of the head on one or both sides.
In adolescent girls or young women, a menstrual period can, rarely, trigger basilar migraine, a throbbing headache on the back of the head, accompanied with blurred vision, slurred speech or other neurological symptoms.
High blood pressure is a rare cause of headache.
Sudden turning of the head in individuals with a pinched nerve in the neck spine can cause sudden pain on the back of the head, usually on one side and abnormal sensations on the same side of the tongue. This is called neck-tongue syndrome.
Chronic Headache
Hats and hair accessories can cause headache on the back of the head. Sleeping without a pillow or the pressure of the head support during driving can also cause repeating headache.
Bad posture, eye strain or other physical or psychological stress can trigger tension headache, pressure-like pain, which can be limited to the back of the head (more or less symmetrically).
A pinched nerve due to chronic disorders of a cervical spine, like spinal arthritis, can cause occipital neuralgia, chronic pain behind one or both ears, aggravated by pressing upon the area. A pinched nerve can also cause tingling in fingers. In myofascial pain syndrome due to shoulder overuse or increased tension in the upper back muscles, trigger points (muscle knots) in the upper back muscles can be identified. Snapping over the trigger points in the upper back can cause pain that radiates to the back of the head. Improving posture and stretching exercises for upper back muscles can help.
In multiple sclerosis, occasional shooting pain on the back of the head may (rarely) occur. Other symptoms include vision problems, tingling and numbness in various parts of the body and other neurological problems. Symptoms come and go throughout the life.
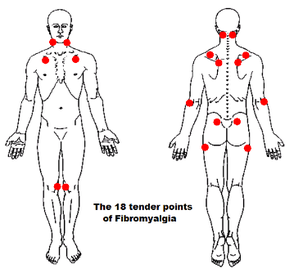
Fibromyalgia is a chronic painful disorder with characteristic tender points in the neck above shoulder blades, on the outer side of the elbows, upper buttocks, hips and knees. Headache is a common associated symptom. The cause is uncertain.
 A cap can cause headache. |
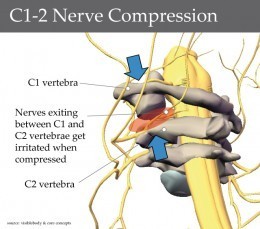 A pinched spinal nerve |
Constant Headache
A brain tumor (right picture) or cyst in the back part of the brain may cause constant headache on the back of the head, usually worse in the morning.
Constipation or dislocated uterus pressing upon the colon can cause constant headache.
Enlarged lymph nodes in throat cancer can cause constant pain at the base of the skull.
Inborn defects of the neck muscles, like torticollis (wry neck) or a cyst (syrinx) in the cervical spinal cord can cause constant headache.
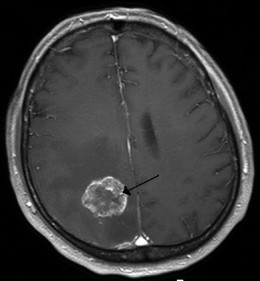 Brain tumor (MRI image) |
Nutrition and Headache
Dehydration. Moderate or severe dehydration can be associated with headache, but not specifically with headache on the back of the head. If you are dehydrated, drinking water may help relieve headache, but if you are well hydrated, additional water will not likely help. Mineral and vitamin deficiencies that may cause headache:
- Iron deficiency with anemia
- Deficiency of various B vitamins
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Severely decreased sodium level in water intoxication often causes headache.
NOTE: If you have normal blood levels of minerals and vitamins, nutrient supplements will not likely relieve headache.
Heavy Metal Intoxication
Chronic intoxication with copper, lead, mercury and other heavy metals may be associated with headache. There is a lot of information online how various cleansing methods can remove heavy metals from your body. If you do not actually have metal poisoning, these methods will not likely help you. It is a licensed doctor who can make a diagnosis of heavy metal poisoning based on blood and urine tests.
How to prepare for a visit to a doctor?
You can write the history of your headache and other health problems in the chronological order - this can greatly help your doctor to make a diagnosis and, eventually, save you some money by avoiding unnecessary investigations.
Try to answer these questions:
- How did headache appear (suddenly, slowly)?
- How long does it last or it lasted (seconds, weeks...)?
- Do you have any tender areas at the back of the head, neck or upper back?
- Do you experience any other symptoms, such as sore throat, toothache, skin rash, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, nausea, fever, blurred vision or memory problems?
- Is your headache associated with a recent event, like injury or menstrual period?
- Do you have any chronic disease?
- Do headaches or chronic diseases run in your family?
You might also like
How to Lower Cortisol Levels Reduce Stress Hormone and Improve...Cortisol is a steroid hormone regulating metabolism, the immune system and ai...
Walking Your Way to HealthThere is much research that shows that walking is beneficial to body and mind.



 Fructose Malabsorptionon 03/19/2016
Fructose Malabsorptionon 03/19/2016
 Scientific Facts About Sugars and Other Sweetenerson 03/17/2016
Scientific Facts About Sugars and Other Sweetenerson 03/17/2016
 Alcohol-Related Headacheon 03/09/2016
Alcohol-Related Headacheon 03/09/2016
 5 Myths About Water Drinkingon 03/09/2016
5 Myths About Water Drinkingon 03/09/2016


Comments
Since injured in a high impact auto accident 6 years ago I have suffered from back of head pain. I sustained spinal cord injury, broken discs and head trauma. This pain is a very horrific thing to live with. I have not taken opioids but instead have acupuncture, walk five miles a day, practice yoga and meditation. It is a delicate balance.,