Bates, Dewonica. Fall 1998. "Mammals at the Fort Worth Zoo: Yellow-Footed Rock Wallaby." Texas Wesleyan University. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.whozoo.org/Intro98/dewobate/dewobates1.htm
Copley, P.; Ellis, M.; and van Weenen, J. 2008. "Petrogale xanthopus." In: IUCN 2008. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/16750/0
Davey, Keith. 2005. "Yellow-footed Rock-wallaby: Petrogale xanthopus." Keith Davey Photo-graphic. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://keith-davey.com/macropods/website/macropods/yellow-foot-rock-wall.htm
Department of the Environment. 2014. "Petrogale xanthopus xanthopus: Yellow-footed Rock-wallaby (SA and NSW)." Species Profile and Threats Database. Canberra: Australian Government. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/sprat/public/publicspecies.pl?taxon_id=66646
Duff, Andrew; and Lawson, Ann. 2004. Mammals of the World: A Checklist. Yale University Press.
Flannery, Timothy F. 1994. Possums of the World: A Monograph of the Phalangeroidea. Chastwood, Australia: GEO Productions in association with the Australian Museum.
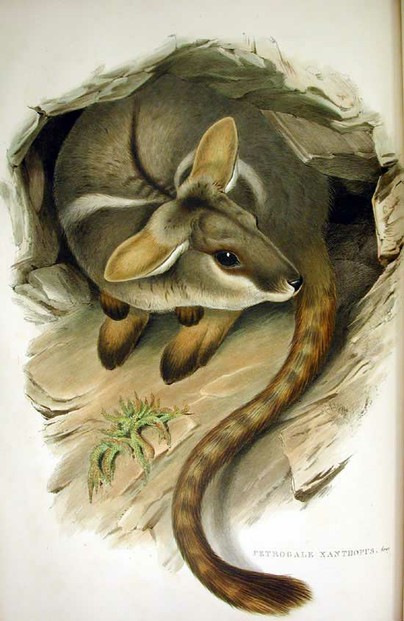
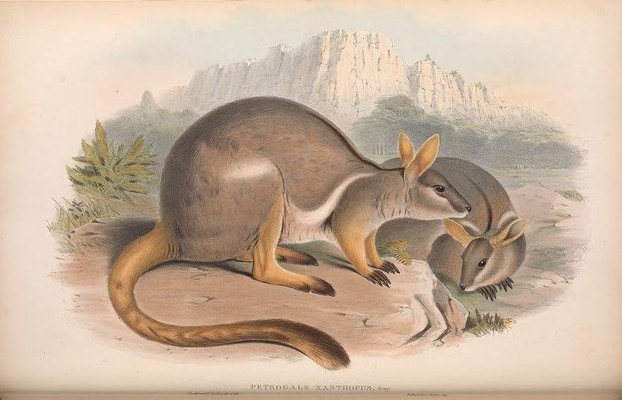
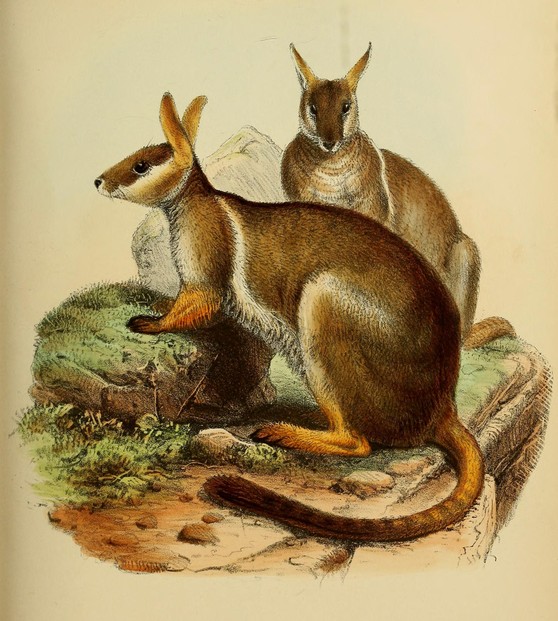
Gould, John. 1863. Mammals of Australia. Volume II. London: John Gould.
- Available via Biodiversity Heritage Library at: https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/49740638
Kerle, Jean Anne. 2001. Possums: The Brushtails, Ringtails and Greater Glider. Sydney: University of New South Wales Australian Natural History Series. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://books.google.com/books?id=YDM0hjAwchUC&lpg=PT65&dq=Petropseudes%20dahli&pg=PT66#v=onepage&q=Petropseudes%20dahli&f=false
"Mammals: Yellow-footed Rock Wallaby." The Animal Facts. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://theanimalfacts.com/mammals/yellow-footed-rock-wallaby/
"Mammals: Yellow-footed Rock-wallaby (Petrogale xanthopus)." OzAnimals Australian Wildlife. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.ozanimals.com/Mammal/Yellow-footed-Rock-wallaby/Petrogale/xanthopus.html
Menkhorst, Peter; and Knight, Frank. 2001. A Field Guide to the Mammals of Australia. South Melbourne: Oxford University Press.
Meredith, Robert W.; Mendoza, Miguel A.; Roberts, Karen K.; Westerman, Michae; and Springer, Mark S. March 2, 2010. “A Phylogeny and Timescale for the Evolution of Pseudocheiridae (Marsupialia: Diprotodontia) in Australia and New Guinea.” Journal of Mammalian Evolution17(2):75-99. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2987229/
Miller, Adrienne. September 1, 2001. "Keeping Yellow-footed Rock Wallabies on the Rocks: Integrating In- and Ex-situ Conservation in Australia and North America." The Free Library Endangered Species Update. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.thefreelibrary.com/Keeping+yellow-footed+rock+wallabies+on+the+rocks%3a+integrating+in-...-a081829317
Nowak, R.M. 1991. Walker's Mammals of the World, Fifth Edition. Volume I. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Nowak, Ronald M. 2005. Walker's Marsupials of the World. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Oldroyd, Ben. 1998. “Pedigree Analysis & The Yellow Footed Rock Wallaby.” SOBSTDU. School of Biological Sciences Teaching Development Unit, University of Sydney. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://bugs.bio.usyd.edu.au/DNA/DNAContents.html
Poole, W.E.; Merchant, J.C.; Carpenter, S.M.; and Calaby, J.H. 1985. "Reproduction, Growth and Age Determination in the Yellow Footed Rock Wallaby Petrogale xanthopus Gray, Captivity." Australian Wildlife Research, Vol. 12, No. 2: 127-136.
"Petrogale xanthopus (Gray, 1854)." ITIS Report. Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=552753
Poland, Henry. Fur Bearing Animals in Nature and in Commerce. London: Gurney & Jackson, MDCCCXCII (1892).
- Available via Internet Archive at: https://archive.org/details/furbearinganimal00polauoft
Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. Illustrations 1848-60. Vol. I: Mammalia. Plates I - LXXXIII. London: Longman, Green, Longmans, and Roberts, n.d. (1861?). Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available via Biodiversity Heritage Library at: http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/37027904
Ride, W.D.L. A Guide to the Native Mammals of Australia. Melbourne: Oxford University Press, 1970.
Steinle, Alison. 2003. "Yellow-footed Rock-wallaby: Petrogale xanthopus (On-line). Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/Petrogale_xanthopus/
Strahan, Ronald; and Conder, Pamela. 2007. Dictionary of Australian and New Guinean Mammals. CSIRO Publishing.
"Wallaby Cliffs: Yellow-footed Rock Wallaby." WILD LIFE Sydney Zoo. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.wildlifesydney.com.au/explore/wallaby-cliffs/wallaby-profile/
"Wildlife and Ecosystems Animals: Yellow-footed Rock-wallaby." Queensland Government Department of Environment and Heritage Protection. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.ehp.qld.gov.au/wildlife/animals-az/yellow_footed_rock_wallaby.html
Wilson, Don E.; and Reeder, DeeAnn M., eds. 1993. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, Third Edition. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
"Yellow-Footed Rock Wallaby." ARKive. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.arkive.org/yellow-footed-rock-wallaby/petrogale-xanthopus/
"Yellow-Footed Rock Wallaby." Los Angeles Zoo & Botanical Gardens Animal Facts. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.lazoo.org/animals/mammals/wallaby_yellowfootedrock/index.html
"Yellow-footed Rock Wallaby: Petrogale xanthopus." P. 97 in Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia, Second Edition. Farmington Hills, MI: Gale Group, Inc. division of Thomson Learning Inc., 2004.
"Yellow-footed Rock-wallaby: Petrogale xanthopus." Featherdale Wildlife Park. Retrieved on February 20, 2014.
- Available at: http://www.featherdale.com.au/wallaby/















 Are Hawaiian Huakai Po Nightmarchers Avenging Halloween Thursday?on 10/02/2024
Are Hawaiian Huakai Po Nightmarchers Avenging Halloween Thursday?on 10/02/2024
 Mailing Addresses for 2023 Form 4868 Extending 1040 and 1040SR April 15, 2024, Due Dateon 04/15/2024
Mailing Addresses for 2023 Form 4868 Extending 1040 and 1040SR April 15, 2024, Due Dateon 04/15/2024
 Mailing Addresses for 2023 Forms 1040 and 1040SR Filed in 2024on 04/15/2024
Mailing Addresses for 2023 Forms 1040 and 1040SR Filed in 2024on 04/15/2024
 Mailing Addresses for 2022 Form 4868 Extending 1040 and 1040SR April 18, 2023, Due Dateon 04/13/2023
Mailing Addresses for 2022 Form 4868 Extending 1040 and 1040SR April 18, 2023, Due Dateon 04/13/2023



Comments
The sixth section advises us that "Alone among mammals, ring-tails know how to transfer water from one mouth to another."
Are other life forms, such as fishes and insects, similarly apt or not?
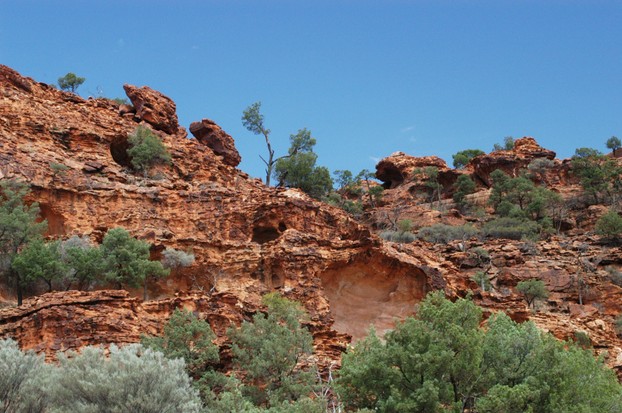
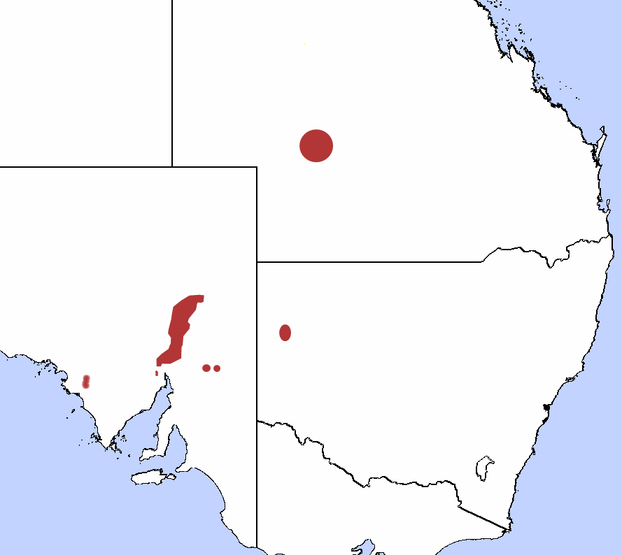
Habitat information between the fourth and fifth images alerts us to "Abundance of bendee and mulga (Acacia spp) leaf litter, forbs (Sida filiformis), rock sedges (Scleria sphacelata), and tufted grasses (Sporobolus caroli); Conglomerate, granite, limestone or sandstone rocky outcrops; Sources of permanent freshwater within 3 miles (4.82 kilometers) of the family home."
Isn't it impelling to imagine a garden inspired by the ring-tailed rock-wallaby habitat iteration?
It might make both a rock- and a water-featured garden in one!
(Of course the permanent freshwater-source would be far, far closer than 3 miles (4.82 kilometers;-D!)
Biogeographical displays advance culinary and landscape aspirations.
Rock gardens number among my arboriculture-adaptable ambiances.
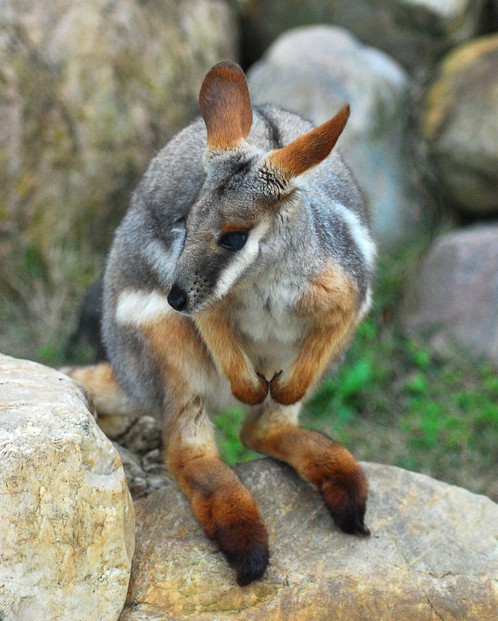
Ring-tailed rock wallabies occur among conglomerate, granite, limestone or sandstone rocky outcrops.
Wouldn't the four afore-observed rock occurrences work wonderfully, wondrously in biogeographical workings for lego and plush-toy ring-tailed rock wallaby displays and models and in rock gardens?
Something that I appreciate at such biogeographical displays as those articulated below are drinkable, edible takeaways as well as such portable and wearable displays as carrying bags and shirts.
The displays concern habitat, predators and preys even as drinkable, edible takeaways consider food sources to conserve.
Ring-tailed rock wallabies eat bark, forbs, fruits, grasses, herbs, roots, shoots and twigs.
Isn't it interestingly intriguing to imagine such edible takeaways as fresh salads of bendee basswood (Tilia americana), mulga (Acacia aneura), nutrush (Scleria sphacelata) flowers, leaves and seeds; of fairy-grass (Sporobolus caroli) cooked seeds; and of wireweed (Sida filiformis) leaves?
The computer crashed before I communicated the complete component of my recentest comment, in the box immediately below.
Rock-haunting ring-tailed possum displays, with or without ring-tailed rock wallabies, deserve their own signs of "Caution! Rock-haunting ring-tailed possum crossing!" They also gain from such signs as "Caution! Put cigars, cigarettes, smokes in ashtrays!" and "Caution! Put out camp fires!"
Predatory people and raging wildfires menace both ring-tailed rock wallaby and rock-haunting wallaby lifespans ;-{.
Ring-tailed land and water animal sentients amaze me.
Isn't it interesting to imagine, in terms of Australian wildlife, such impressive sentients as ring-tailed rock wallabies and rock-haunting ring-tailed possums invoked through museum and school displays of lego or plush toys with each species' comparative family and friends, homes and hideouts, predators and prey?
Ring-tailed rock wallabies encourage me to elaborate, imaginatively if not actually, museum and public-institution displays of plush-toy ring-tailed rock-wallabies in an accurate reconstruction of their homeland environments, with signs like "Caution! Ring-tailed rock wallaby crossing!"
Another sign pertinent to their homelands and their lifestyle is "Caution! Put cigars, cigarettes, smokes in ashtrays!" Yet another is "Caution! Put out camp fires!"
Predatory people and raging wildfires menace ring-tailed rock wallaby lifespans ;-.
Mira, I try not to scrutinize feeding chains and food webs too closely when it comes to adorable animals!
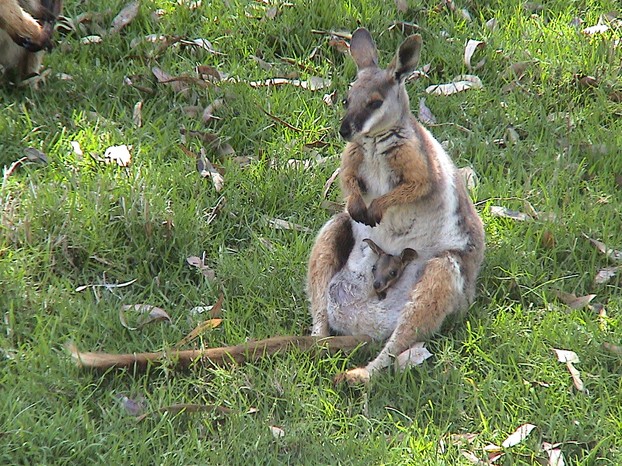
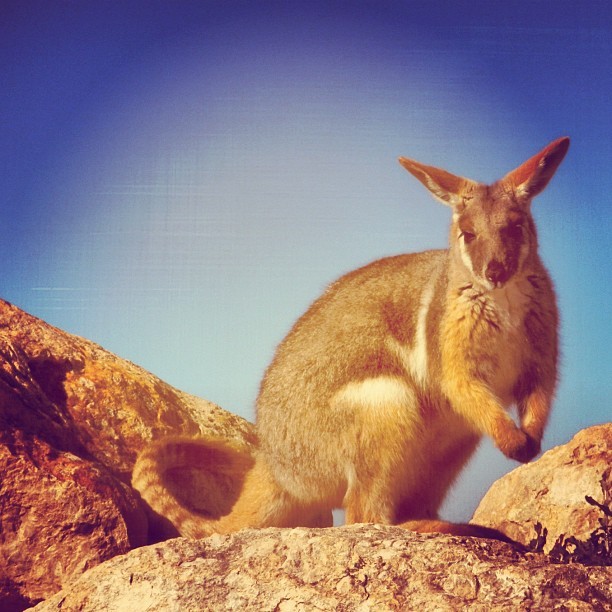
Wallabies are so cute! I especially liked that photo with the joey (new word for me) in the marsupium. I'm surprised at their land distribution though. I would have expected their habitat to be much larger.
P.S. Sad to learn they fall prey to dingoes!