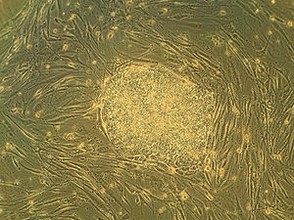
Adult stem cells (ASCs) are stem cells found in juvenile and adult individuals whereas embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are stem cells found, as suggested by their name, in embryos.
ASCs are mainly responsible for replenishing and regenerating dying cells and tissues. On the other hand, ESCs participate in the process of embryogenesis. All tissues and organs are initially created by ESCs.
As mentioned before there is also a third type of stem cells, called induced pluripotent stem cells. These stem cells don’t occur naturally and are created in the lab via a method called transfection. Essentially, they are somatic cells (specialized cells like neurons) that have been reversed to a stem cell-like nature. They are pluripotent and very similar to ESCs.
Stem cells have two specific attributes that make them unique when compared to other types of cells. The first attribute is called potency and the second self-renewal.


 Dog Training: Essential Equipmenton 12/14/2016
Dog Training: Essential Equipmenton 12/14/2016
 12 of the World's Weirdest Animalson 11/30/2014
12 of the World's Weirdest Animalson 11/30/2014
 Promachoteuthis sulcus: Strange Squid with human like teethon 04/10/2014
Promachoteuthis sulcus: Strange Squid with human like teethon 04/10/2014
 Autologous Matrix Induced Chondrogenesison 04/10/2013
Autologous Matrix Induced Chondrogenesison 04/10/2013


Comments
Stem cells in itself is a word more commonly spoken and yet there is rarely a good description as to what these vital cells actually are and what they can do. It's still a topic needed more light shed on it. You've done a very good job of clearing any confusion I had as to the what and why of stem cells I thank you. :)K