Astronomy defines the Southern sky as the half of the celestial sphere that is south of the celestial Equator.
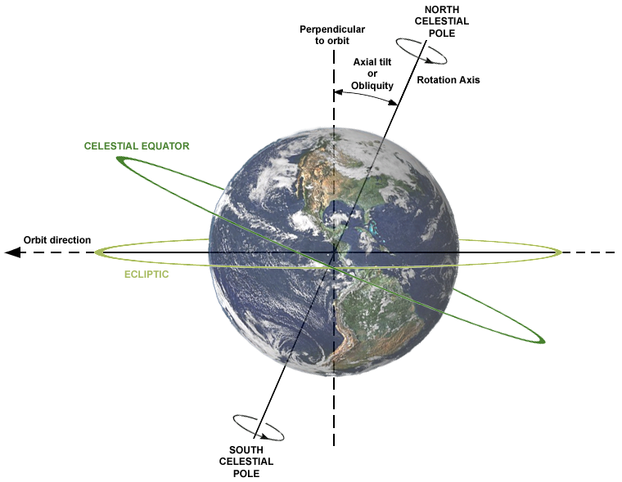
The Earth's axial tilt is responsible for the celestial Equator's inclination by 23.4° with respect to the ecliptic plane.
axial tilt (or obliquity), rotation axis, plane of orbit, celestial equator and ecliptic; Earth viewed from Sun: Dennis Nilsson, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons @ https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:AxialTiltObliquity.png
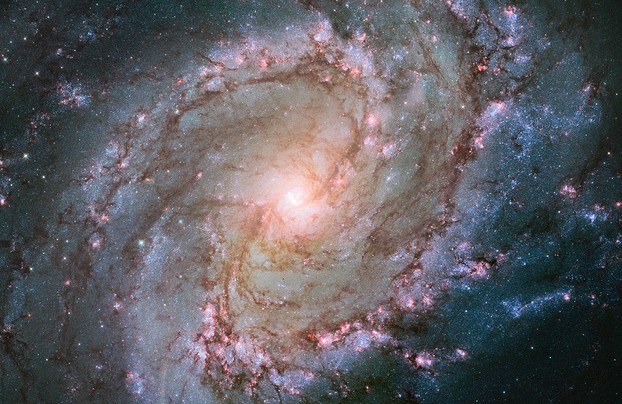
Southern Pinwheel Galaxy, also known as Messier 83, M83, or NGC 5236, is visible with binoculars.
On February 23, 1752, French astronomer Abbé Nicolas Louis de La Caille (December 28, 1713 – March 21, 1762) discovered the barred spiral galaxy at the Cape of Good Hope.
Southern Pinwheel Galaxy, distanced 15 million light years, in Hydra the Sea Serpent constellation; image released Jan. 9, 2014: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA); Acknowledgement William Blair (Johns Hopkins University), Public Domain, via Wikimedia Commons @ https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hubble_view_of_barred_spiral_galaxy_Messier_83.jpg
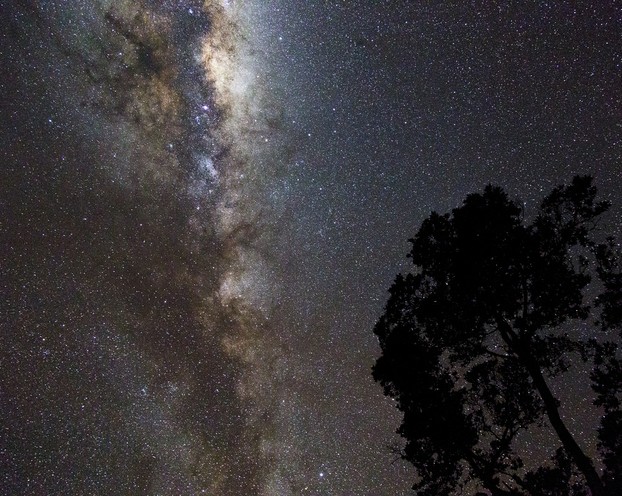
Milky Way Galaxy and the pōhutukawa (Metrosideros excelsa), also known as New Zealand Christmas tree
Okato, Taranaki, western North Island, New Zealand: Dave Young (dcysurfer / Dave Young), CC BY 2.0, via Flickr @ https://www.flickr.com/photos/dcysurfer/14783345783/
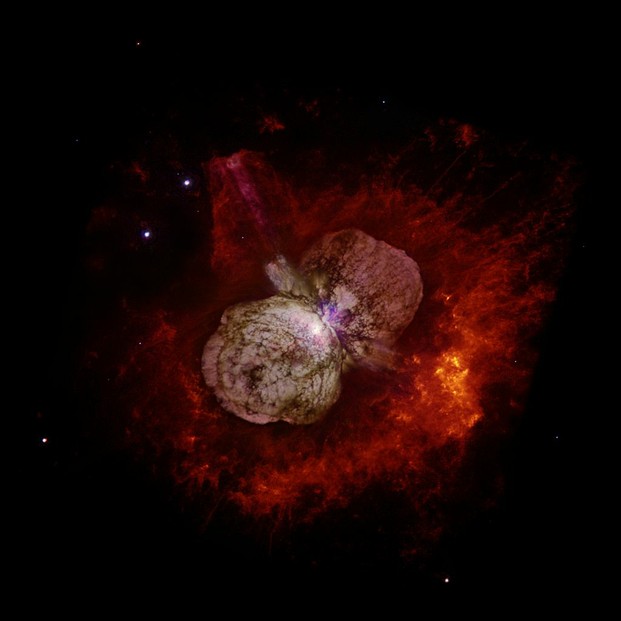
Eta Carinae is surrounded by Homunculus Nebula, a bipolar (bi-lobed) reflection nebula that in turn is embedded with the Eta Carinae nebula.
Image was taken through red and near-ultraviolet filters to capture the dynamic range of central star glaring 100,000 times more brightly than the faint outer ejecta blobs.
Hubble's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2), September 1995: Nathan Smith (University of California, Berkeley), and NASA, Public Domain, via Wikimedia Commons @ https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:EtaCarinae.jpg
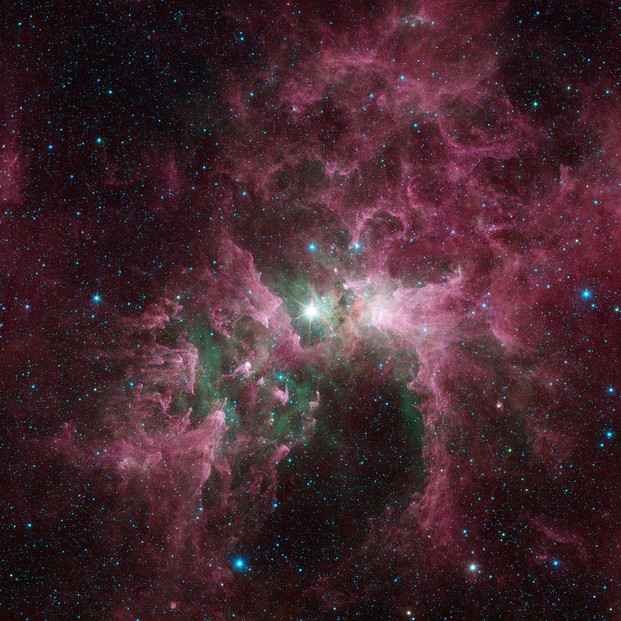
Eta Carinae nebula: never visible north of 30°North latitude; visible circumpolar south of 30°South latitude
Namesake blinding star at nebula's center has mass 100 times that of Earth's Sun; the star's infrared light destroys particles of nebular dust, sculpting cavities and leaving pillars of denser material pointing back to the star.
the tortured clouds of Eta Carinae, viewed from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope: NASA/JPL-Caltech, Public Domain, via Wikimedia Commons @ https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:The_Tortured_Clouds_of_Eta_Carinae.jpg














 Are Hawaiian Huakai Po Nightmarchers Avenging Halloween Thursday?on 10/02/2024
Are Hawaiian Huakai Po Nightmarchers Avenging Halloween Thursday?on 10/02/2024
 Mailing Addresses for 2023 Form 4868 Extending 1040 and 1040SR April 15, 2024, Due Dateon 04/15/2024
Mailing Addresses for 2023 Form 4868 Extending 1040 and 1040SR April 15, 2024, Due Dateon 04/15/2024
 Mailing Addresses for 2023 Forms 1040 and 1040SR Filed in 2024on 04/15/2024
Mailing Addresses for 2023 Forms 1040 and 1040SR Filed in 2024on 04/15/2024
 Mailing Addresses for 2022 Form 4868 Extending 1040 and 1040SR April 18, 2023, Due Dateon 04/13/2023
Mailing Addresses for 2022 Form 4868 Extending 1040 and 1040SR April 18, 2023, Due Dateon 04/13/2023



Comments
The computer crashed afore I could communicate another component of Southern-Hemisphere sky charts.
The ancient Hawaiian and the ancient Polynesian cultures connect.
Mightn't it be miraculously marvelous to make a series of Southern-Hemisphere sky maps about the manners and modes whereby each Hawaiian-, each Polynesian-island culture manifests navigational star-family star lines?
Wouldn't that work wonderfully, wondrously as a wallpapered corner to a business, home, library, museum, school display?
The Southern-Hemisphere star chart above, as last in this wizzley-related product line, causes me to consider a poster series of the star arrangements from the various pre-Hispanic cultures of the Southern-Hemisphere countries (Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay, Bolivia).
Mightn't that make for a miraculous marvel to mural a business/library/museum/school -- or home audio-visual, library, rec room -- display corner with a Southern-Hemisphere series of sky charts from Aymara-, Guarani-, Runa Shimi-, Tupi-speaking cultures?
February 2026 invites those intent upon binocularly, telescopically, visually itinerating dark skies even as it invokes certain planetary itineraries over Hawaiian-archipelagic skies.
The planet Jupiter, as Ka'āwelo in Hawaiian, journeys beautifully near the sky center over the Hawaiian islands.
Might all these Jupiter-ian marvels that never manifested previously in our astronomical-observation meanderings make the gas giant matter even more to those managing dark-sky monitoring?
A dream book is one that integrates the Polynesian voyaging tradition of ancient Hawaiians even as traditional Hawaiians invoke the afore-indicated people's ideating constellation iterations that sometimes, sometimes not include the mainland-Unitedstatesian identifications.
For example, the above text initiates with "Southern skies are less cluttered nightly than northern."
Hawaiian-night skies of February 2026 jubilate one star line, Kekaomakali'i/the Makalii Bailer even as that navigational star-family joins among its star-line stars such stars as 'A'ā/Sirius and the Nāmāhoe/Twins Nānāmua/Castor and Nānāhope/Pollux.
Those skies keepsake the Milky Way from the Ho'olau/northwest to the Malanai/southeast horizons.
Bernice Pauahi Bishop Museum currently lodges the February 2026 sky map for downloading. How about trying that sky map of Hawaiian-skied galaxies, star lines and stars during this tidy-sky time?
The Bernice Pauahi Bishop Museum of Honolulu, Oahu island, Hawaii state and the 'Imiloa Astronomy Center of Hilo, Hawaii County, island and state construct respectively monthly sky maps and sky charts.
Could some agency or company or institution consider likewise for southern-skied Africa and America?