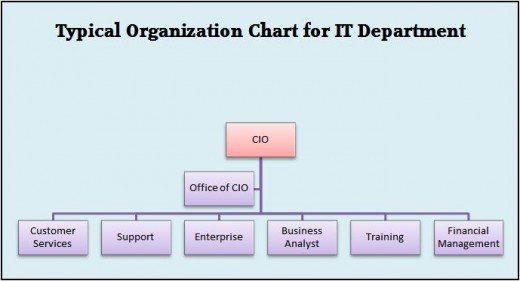
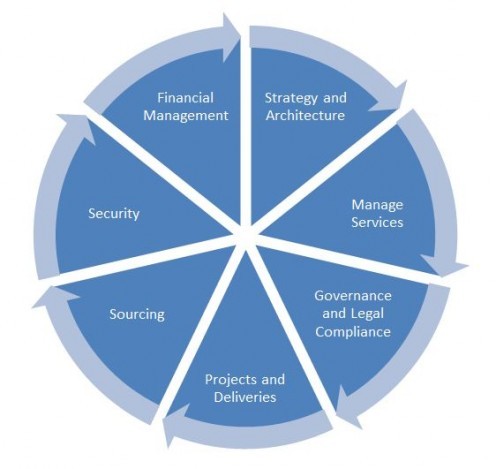
The CIO (Chief Information Officer) is typically the head of information technology (IT) within a corporation or organization. The CIO is a leadership position that reports directly to the Chief Financial Officer or, in many cases, the Chief Executive Officer.
The job of the CIO is to ensure that the information technology and computer systems support the corporation and assist in reaching business and enterprise goals. IT systems have become far more important to modern businesses and the CIO has become a very strategic role that helps leaders formulate a business plan and strategy incorporating modern technologies.
The CIO is a high level position in which analysis of business processes is a key function allowing for the company to develop cohesive plans to use new technology to improve functionality of the business as a whole.
Often a modern CIO will have business acumen, organizational skills, and project management skills in addition to IT skills. The combination of these elements allows for a deeper understanding of the corporate world as well as the IT world given leadership far more insight into the way technology can change the way things are done without compromising quality.




 Top Next Generation Consoles in 2014on 05/15/2014
Top Next Generation Consoles in 2014on 05/15/2014
 Top Science Fiction and Fantasy Authorson 05/14/2014
Top Science Fiction and Fantasy Authorson 05/14/2014
 Guest Posting - are they worth it?on 06/20/2011
Guest Posting - are they worth it?on 06/20/2011
 Where can I earn money by writing on the web?on 06/10/2011
Where can I earn money by writing on the web?on 06/10/2011



Comments